Value Mapping
Value mapping allows you to map specific source values to target values without writing complex expressions. Use it when:
- Applying matching rules for specific values.
- Mapping picklist (enum) item values.
- Converting data types.
For example, you can use value mapping to map the Status field when creating new Salesforce cases from Zendesk tickets. Status is the picklist (enum) field with a predefined set of possible values. Despite Salesforce and Zendesk have different possible Status values, with value mapping you can easily match the statuses between both platforms.
Value mapping is available for the Column and Lookup mapping types only.
How to Map Values
-
On the Mapping Definition page of the task editor, select the Column or Lookup mapping and click Map values.
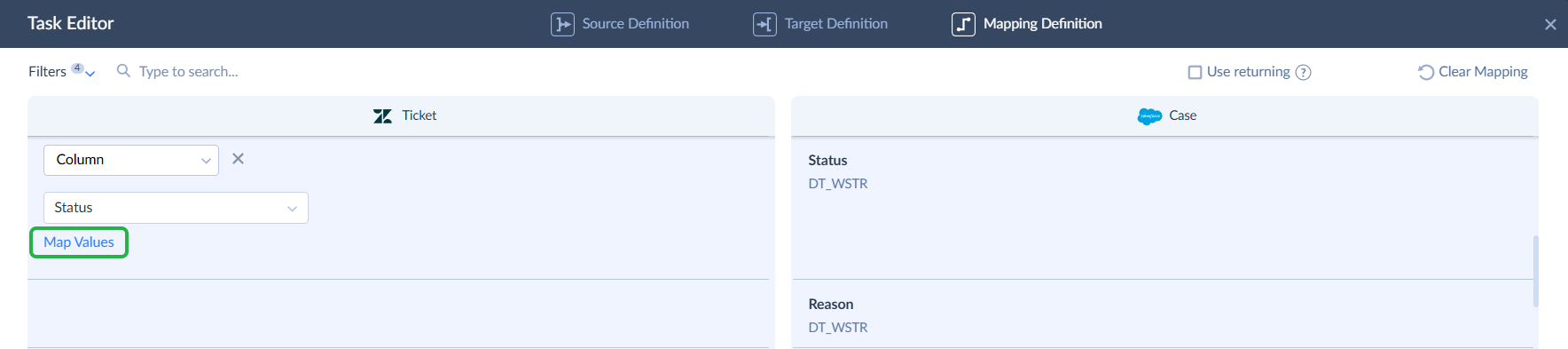
-
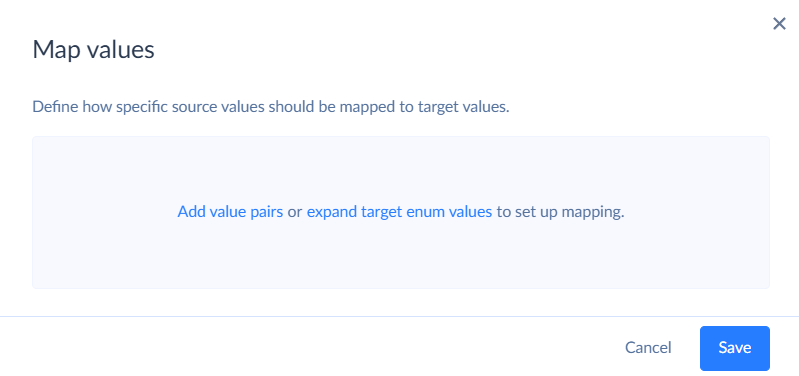
Click Add value pairs to configure source-to-target value mapping. If the target field is an enum, click expand target enum values to get quick access to the picklist item values in target.
-
Optionally, set the Unmapped value behaviour and click Save.
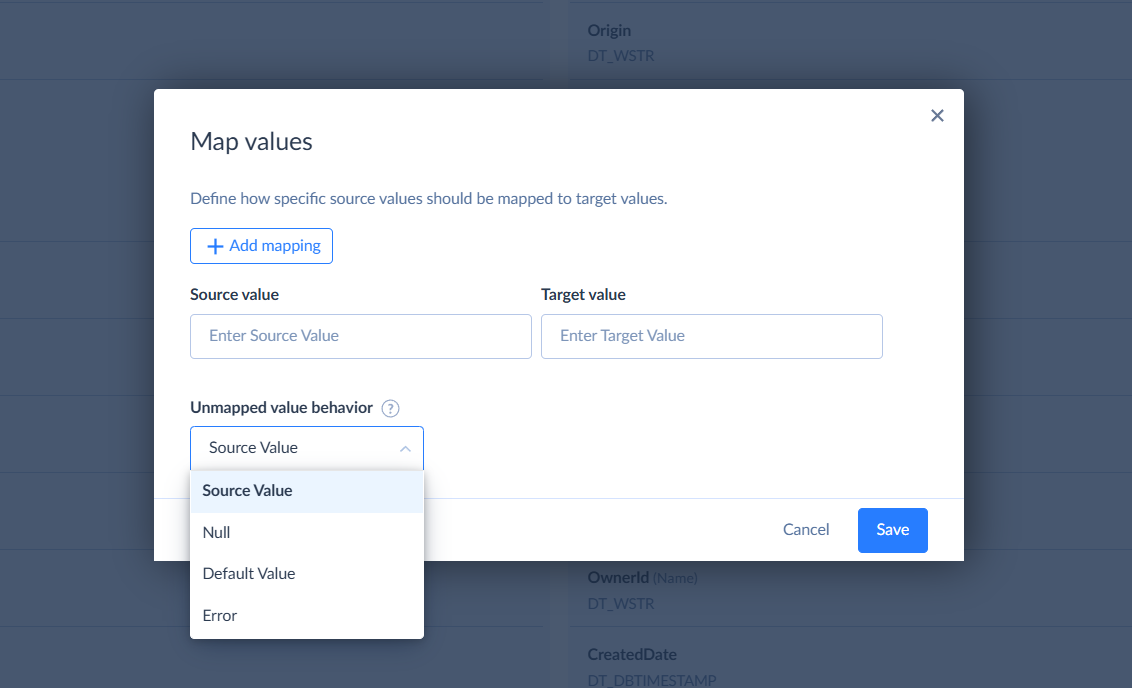
Unmapped Value Behavior
Unmapped value behavior defines how Skyvia treats source values not listed in the value mapping.
| Behaviour | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Value | Maps the unlisted source value as it is |
| Null | Maps NULL |
| Default Value | Maps a specific value defined by the user |
| Error | Returns an error for a record that contains the unlisted value |
Data Types
You can use Value Mapping with source and target fields of the following data types: DT_STR, DT_WSTR, DT_I1, DT_I2, DT_I4, DT_I8, DT_R4, DT_R8, DT_CY, DT_GUID, DT_DECIMAL, DT_NUMERIC.
Combine values of these types in Value Mapping using various combinations, for example, DT_WSTR -> DT_WSTR, DT_I4 -> DT_WSTR, DT_WSTR -> DT_I4, DT_I4 -> DT_I4, etc.