Amazon S3
Amazon S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service) is a cloud storage service offered by Amazon (AWS). It stores data as objects, hierarchical data, or tabular data within buckets.
You can use Amazon S3 as a source for Import, as a target for Export, and as source and target for Data Flow.
Establishing Connection
To create connection to Amazon S3 server, specify the S3 Region to use AWS Access Key ID and AWS Secret Key. For temporary credentials you need to specify AWS Security Token. You also need to specify the S3 Bucket Name to upload file to.
Creating Connection
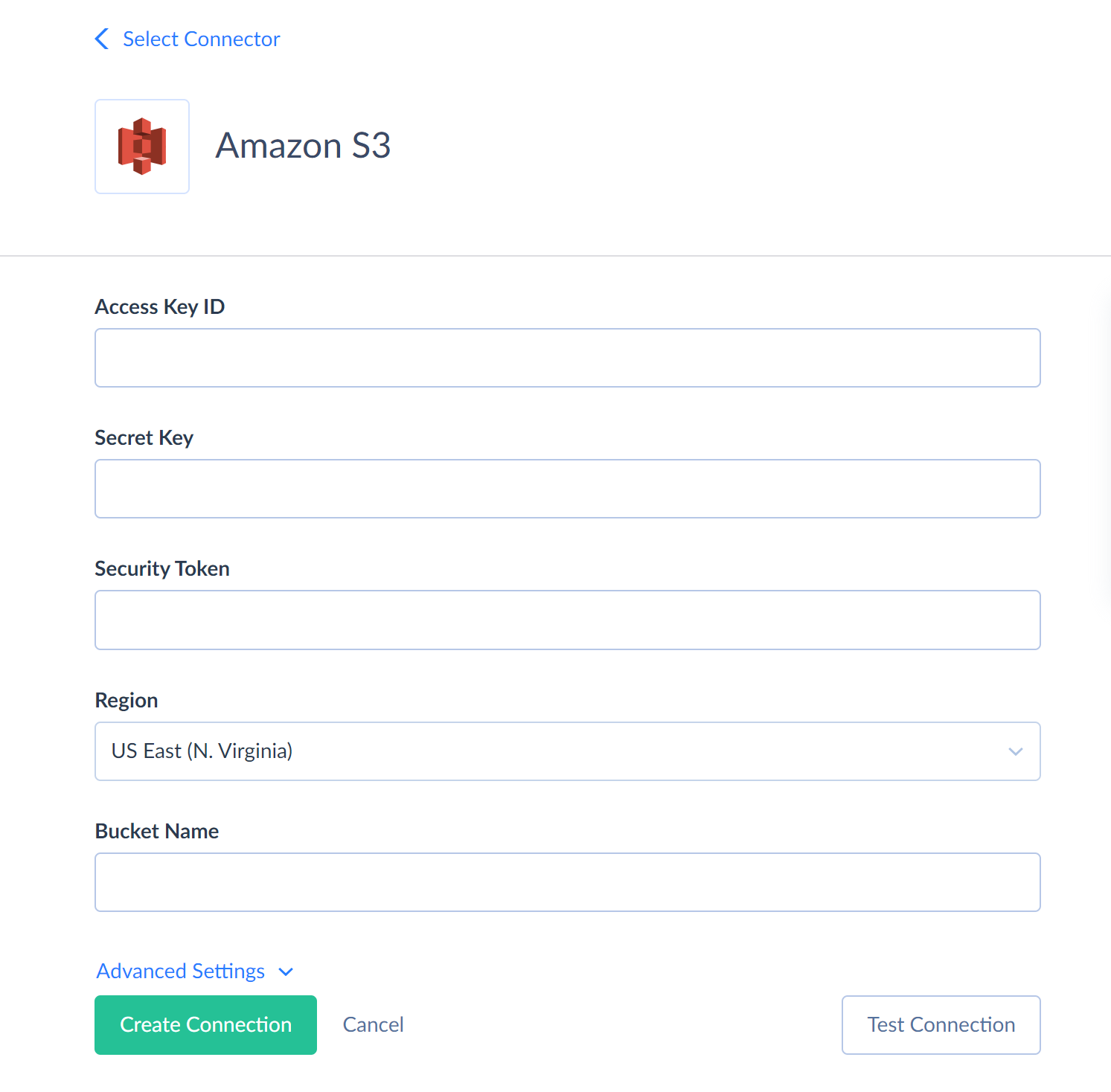
You need to specify the following parameters for Amazon S3 connection:
- Access Key ID — first part of your Amazon Web Services access key.
- Secret Key — second part of your Amazon Web Services access key. Read more about AWS access keys...
- Security Token — session token used with temporary security credentials. Read more about temporary credentials...
- Region — AWS region, where your S3 storage is hosted.
- Bucket Name — the name of your S3 bucket to load CSV files from or to.
Additional Connection Parameters
Working Directory is a path in the Amazon S3 bucket to use as a root folder in Skyvia. You can use this parameter, when you only have access to a specific folder in the Amazon S3 bucket, and cannot access bucket root. You should not use bucket name in this parameter.
For example, if you have access to bucket/folder/subfolder where bucket is the bucket name, you should set Working Directory to folder/subfolder, and set Bucket Name to bucket.
Connector Specifics
File Masks
When you use Amazon S3 as CSV source, you can specify a file mask using a date/time template instead of selecting a file. When integration runs, it will search the file in the folder by substituting the current date to the mask.
Storage for Bulk Loads
You can use Amazon S3 for as file storage for bulk loads for Snowflake and Amazon Redshift connectors.
Useful Links
Amazon S3 integration tutorials