Notion
Notion is an all-in-one platform for individuals and teams to organize thoughts, plans, and workflows.
Data integration: Skyvia supports importing data to and from Notion, exporting Notion data to CSV files, replicating Notion data to relational databases, and synchronizing Notion data with other cloud apps and relational databases.
Backup: Skyvia Backup does not support Notion.
Query: Skyvia Query supports Notion.
Establishing Connection
To create a connection to Notion, you can use OAuth 2.0 or Internal Integration Token authentication type.
Getting Credentials for Internal Integration Token Authentication
Creating Integration in Notion
-
Go tohttps://www.notion.so/profile/integrationsand clickNew Integration.
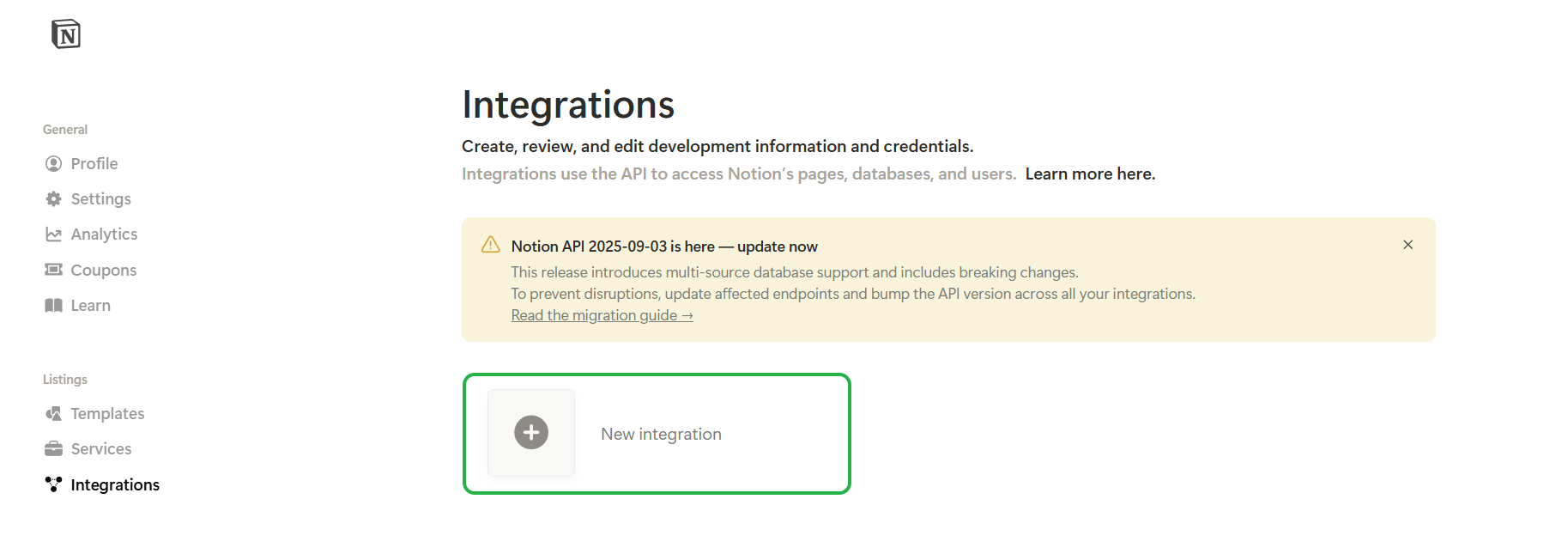
-
Enter integration name, select integration type, save the integration, and click Configure integration settings.
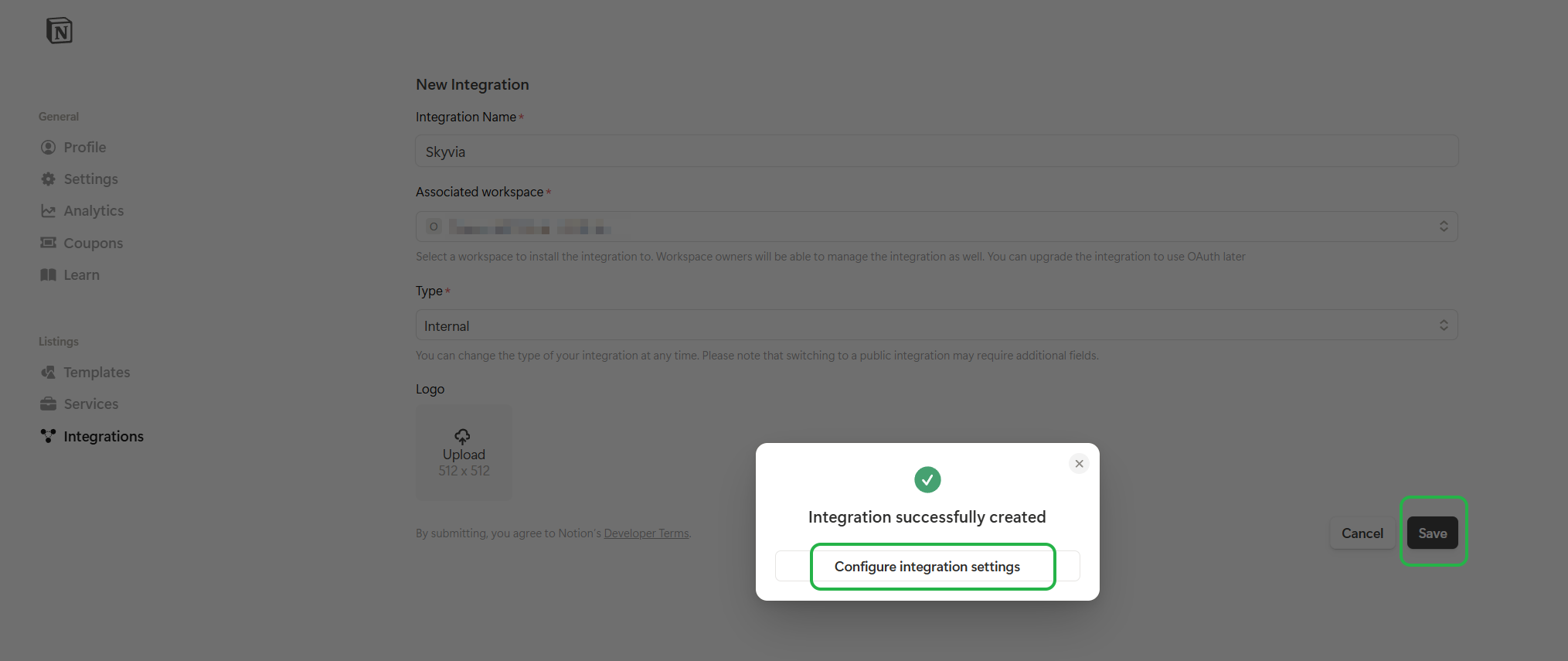
-
Switch to the Access tab and click Select pages.
-
Choose the pages or databases that this integration can access.
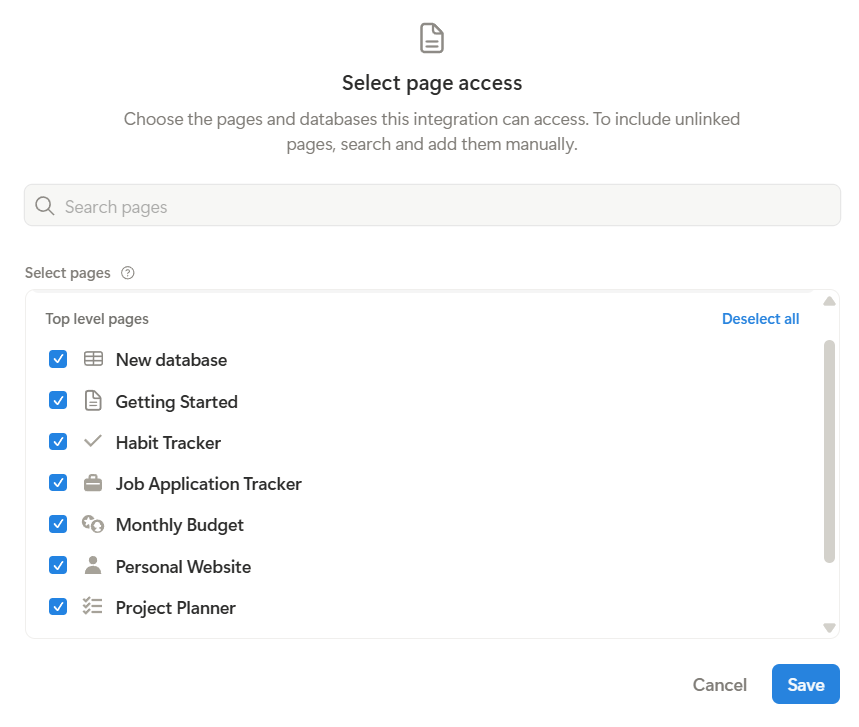
Getting Internal Integration Token
- Go to https://www.notion.so/profile/integrations and open the desired integration.
- Copy the Internal Integration Secret.
Creating Internal Integration Token Connection
To connect to Notion using an Internal Integration Token, enter the obtained token into the Integration Token box in the Connection Editor.
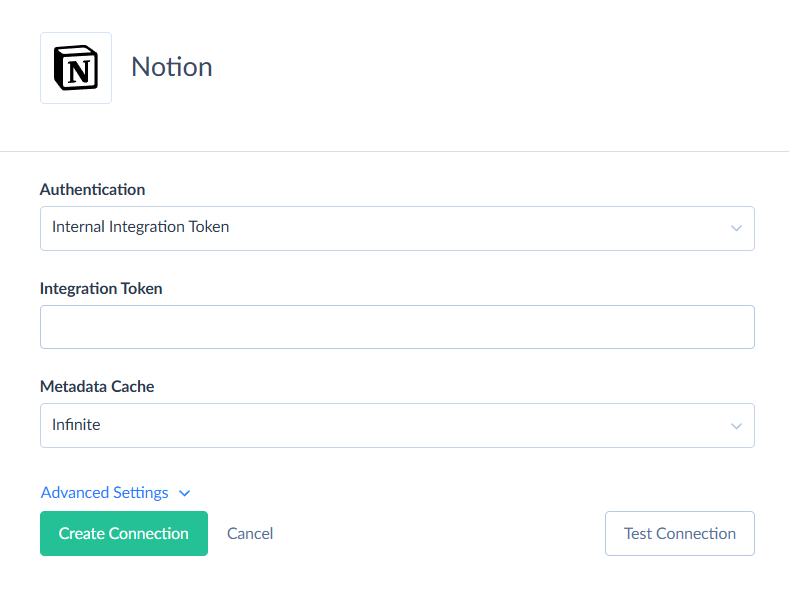
Creating OAuth 2.0 Connection
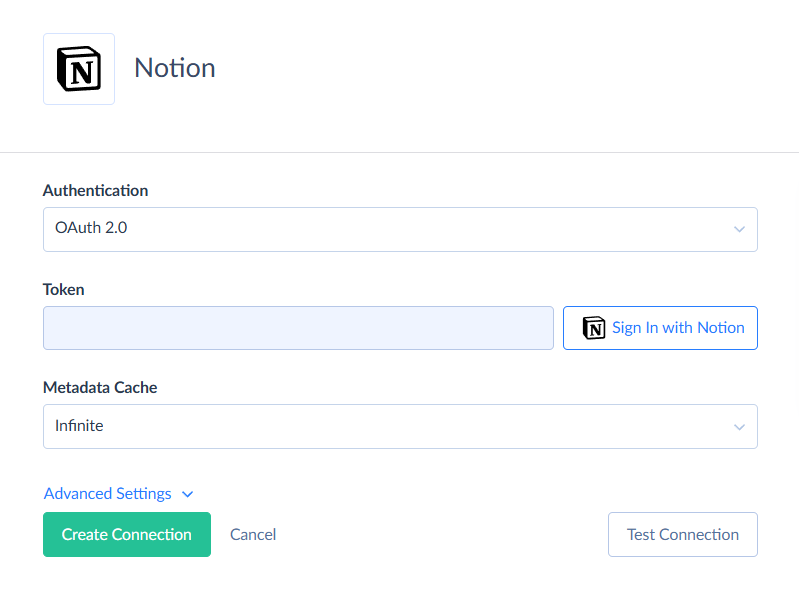
To connect to Notion using OAuth 2.0, perform the following steps:
-
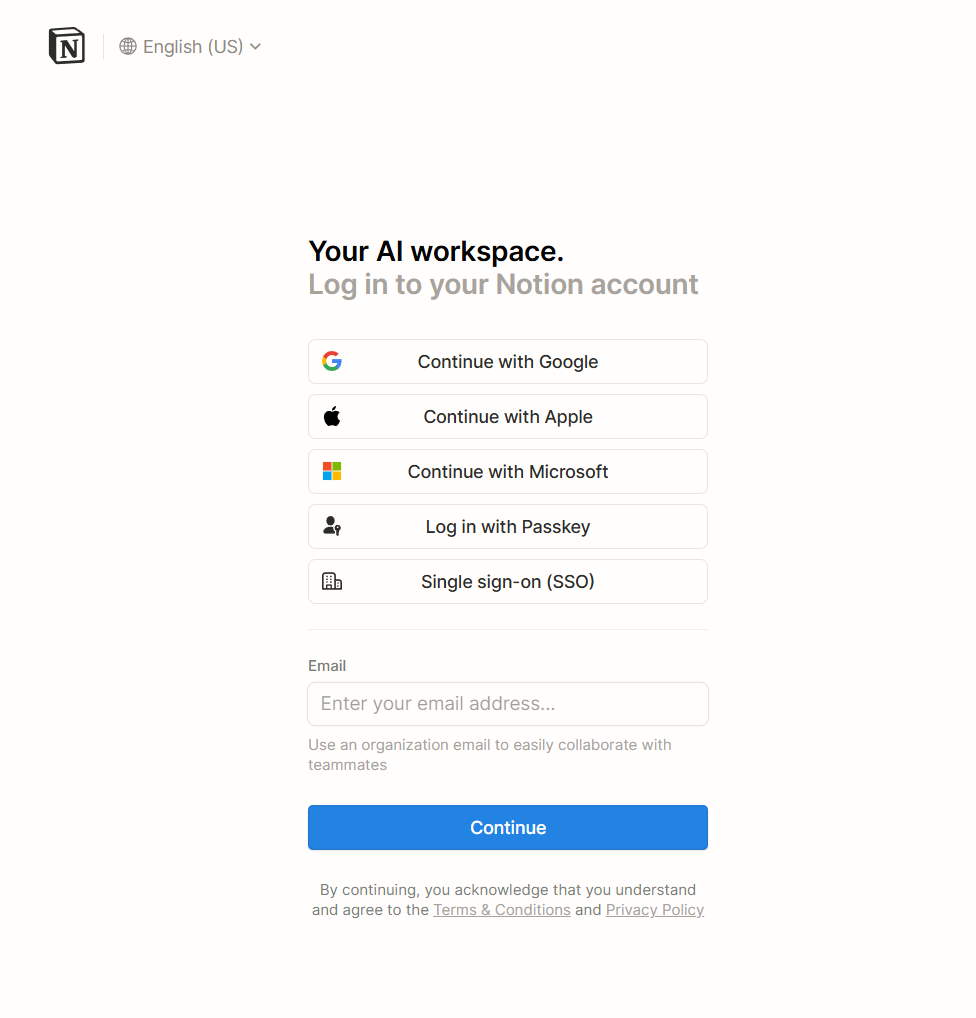
Click Sign-in with Notion and sign in using your credentials.
-
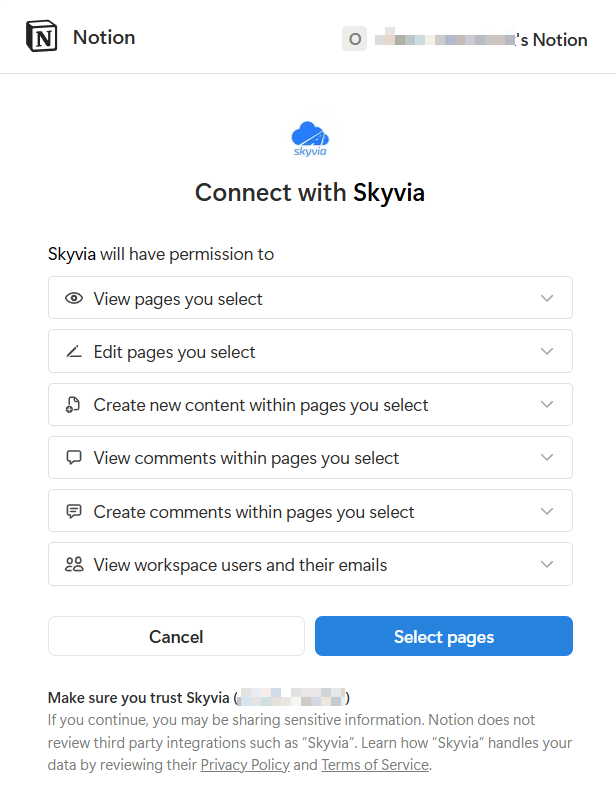
ClickSelect pages.
-
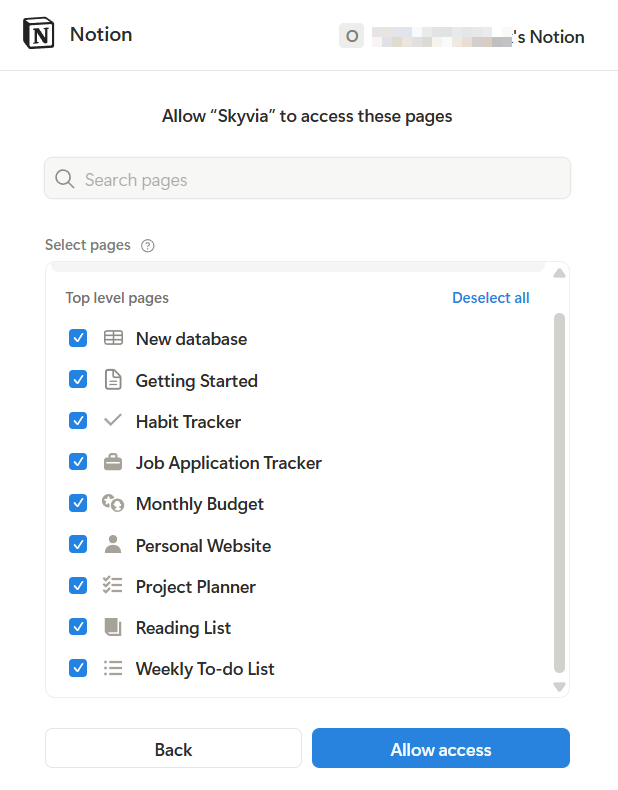
Select the pages to allow access to.
Additional Connection Parameters
Suppress Extended Requests
Notion API returns only part of the fields for some objects when querying multiple records. Skyvia performs additional extended requests to query the values of missing fields. Skyvia performs such API requests for each record of such an object. However, this can decrease performance and significantly increase the number of API calls used.
The additional fields are the following:
| OBJECT | FIELD |
|---|---|
| Database objects | Relation if contains 25+ links |
To reduce the number of API calls, you can select the Suppress Extended Requests checkbox.
Metadata Cache
You can specify the period of time, after which metadata cache is considered expired.
Connector Specifics
Object Peculiarities
Database Objects
Objects in the connector are dynamic. Object names are formed of user names or generated based on a database identifier in the Database_{DatabaseId} format.
Every object contains a set of static fields and dynamic fields.
Static fields: Id, CoverUrl, CoverContent, CoverFileName, IconEmoji, IconUrl, IconContent, IconFileName, RowUrl, RowPublicUrl, CreatedBy, UpdatedBy, CreatedDate, UpdatedDate.
Dynamic fields
Notion supports the following dynamic field types.
| Notion Type | DbType | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text | DbType.String / Complex TextType | Splits into 2 fields: {Name}_PlainText (ReadOnly, length 1000) and {Name}_RichText of complex type TextType (length Int32.MaxLength). |
| Number | DbType.Decimal | |
| Select | DbType.String | Enum field, length is calculated but not less than 120. |
| Status | DbType.String | Enum field, length is calculated but not less than 120. |
| Multi-select | DbType.String | MultiEnum field, length is calculated but not less than 255. |
| Date | DbType.DateTime | Splits into 2 fields: {Name}_Start and {Name}_End. |
| Person | Complex PeopleType | Length Int32.MaxLength. |
| Files & media | Complex FileAndMediaType | Length Int32.MaxLength. |
| Checkbox | DbType.Boolean | |
| URL, Email, Phone | DbType.String | Length 1000. |
| Relation | Complex RelationType | Length Int32.MaxLength. |
| Formula | DbType.String | Splits into 2 fields: {Name}_FormulaType (ReadOnly, length 1000) and {Name}_FormulaValue (ReadOnly, length 1000). |
| Rollup | DbType.String | Splits into 3 fields: {Name}_RollupType (ReadOnly, length 1000), {Name}_RollupValue of type DbType.String, ReadOnly, length 1000; and {Name}_RollupFunction of type DbType.String, ReadOnly, length 1000. |
Comment Objects
For each dynamic database object, Skyvia creates a separate comment object. The object names consist of the corresponding database name with the *Comments suffix.
When inserting data into this object, the DisplayNameType field can accept one of these values:
- Custom. The DisplayNameResolvedName field is also required for mapping.
- User. It is used for public integrations only. The DisplayNameResolvedName value is set by Notion automatically and contains the user’s name. You cannot change this value using the INSERT operation.
- Integration. The DisplayNameResolvedName is set by Notion automatically and contains the integration name. You cannot change this value using the INSERT operation.
Rich Text Field
The fields of the RichText type in dynamic objects has a complex structure. It splits into two related fields:
{Name}_PlainText — plain text, aggregated from an array.
{Name}_RichText — a nested array of objects, where each describes a separate fragment of text.
For example, a string of three words in a Text field may be represented either as a single element or as three separate objects.
Structure of Rich Text Elements
Each element may consist of three main types, each with its own fields:
| Type | Subtype | Fields / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| text | – | Text_Content, Text_Link |
| mention | database | Mention_DatabaseId |
| date | Mention_DateStart, Mention_DateEnd | |
| link_preview | ReadOnly | |
| page | Mention_PageId | |
| template_mention | ReadOnly | |
| custom_emoji | Mention_CustomEmoji_Id | |
| user | Mention_UserId | |
| equation | – | Equation_Expression |
Each element can contain an annotations description (bold, italic, strikethrough, underline, code, color), regardless of its type.
A single Rich text field may contain multiple elements of different types (for example, the first — text, the second — equation)
It is recommended to insert a complete set of data corresponding to the element’s type or subtype. Mixing multiple types within the same element may cause errors, or Notion may ignore part of the data. To insert data into a RichText field, provide the value in JSON format or enable the Nested Objects option in Import and map the nested elements directly.
Dynamic Files & media Objects
Files & media fields have a complex JSON Array structure. For user convenience, Skyvia represents the nested array items as separate objects. The object names consist of the corresponding object name and the *FieldName suffix.
When you insert files to such objects, consider the following:
- Insert one file per record. An attempt to insert more than one file will fail with an error.
- When inserting a file, Skyvia performs an additional API call to check if a file already exists in this field for the given record.
Adding Files to Files & media Fields
You can add multiple files or update data in such fields, using the dynamic database objects. To do that, map the Files & media field using the following methods:
- Provide the value in JSON format specifying the file name and either a public URL of the required file
[{"Name":"some-file-name.png","Url":"https://www.some-url.com//some-file-name.png"}]or the FileUploads upload record ID value, if it exists. You can creatw a file upload using the corresponding stored procedure. - Enable the Nested Object option in import and map the Name and either Url or FileUploadId fields directly.
Objects with Binary Fields
The following Notion objects contain the binary fields:
- Database objects:
CoverContent,IconContent - Files & media objects:
Content - Users:
AvatarContent
If you query these fields, Skyvia performs additional API calls for each record to load the binary content, which may significantly slow query performance.
Adding Binary Content
To add binary content like a cover, icon, or avatar, you can map either the file URL or a file itself with its name. Each set of binary fields has two options for use.
To add a cover file, use the following methods:
- Specify a public link in the CoverUrl field.
- Specify the binary content in the CoverContent together with the file name in the CoverFileName field.
To add an icon file, use the following ways:
- Specify a public link in the IconUrl field.
- Specify the binary content in the IconContent together with the file name in the IconFileName field, and IconEmoji field.
- Specify the emoji character in the IconEmoji field.
Filtering Specifics
Notion API supports the following native filters:
| Object or Object Type | Field or Field Type | Operator |
|---|---|---|
| Database objects | Id | = |
| CreatedDate, UpdatedDate | =, <, <=, >, >= |
|
| URL, Email, Phone, Select, Status | =, !=, IsNull, IsNotNull |
|
| Number | =, !=, <, <=, >, >=, IsNull, IsNotNull |
|
| Person, Files & media, Relation, Multi-select | IsNull, IsNotNull |
|
| Date_Start | =, IsNull, IsNotNull, <, <=, >, >= |
|
| Checkbox | =, != |
|
| ID | =, !=, <, <=, >, >= |
|
| Comment objects, Files & Media objects | RowId | = |
| Users | Id | = |
| FileUploads | Id, Status | = |
Use these filters to improve performance and save API calls. You can use filters with other fields or operators, but it may increase API call usage.
Nested Objects (or separate object name)
Notion *RichText and *Files&media fields store complex structured data in JSON format. You can use our Nested Objects mapping feature in the Import integrations to insert or update the nested values in such fields. Select the Separate Tables for the Unwind Nested Objects option when using the new replication runtime to replicate the nested data into separate tables.
Incremental Replication and Synchronization
Skyvia supports Replication with Incremental Updates for the objects that contain either CreatedDate or UpdatedDate fields.
Skyvia supports Synchronization for the objects that support Incremental Replication and the INSERT and UPDATE operations.
DML Operations Support
| Operation | Object |
|---|---|
| INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE | Database dynamic objects |
| INSERT | Comment dynamic objects, dynamic Files & media objects |
Stored Procedures
Skyvia represents part of the supported Notion features as stored procedures. You can call a stored procedure, for example, as a text of the command in the ExecuteCommand action in a Target component of a Data Flow or in Query.
FileUpload
To create a new file upload, use the following command:
call FileUpload (:filename, :content)
| PARAMETER NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| FileName | Name of the file to be created. |
| Content | Binary content or base-64 value. |
Supported Actions
Skyvia supports all the common actions for Notion.